Advancements in solid lubricant materials are critical for enhancing the performance of solid-lubricating bearings in high-speed applications. High-speed environments pose challenges like increased frictional heat, wear, and reduced efficiency, requiring innovative solutions. Here are some key advancements:
Nanotechnology in Solid Lubricants
Nanocomposites: Combining traditional solid lubricants like graphite or molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) with nanoparticles (e.g., graphene, carbon nanotubes) can enhance their thermal stability and wear resistance.
Benefits for Bearings: Solid-lubricating bearings with nanocomposite coatings can operate more effectively at high speeds due to lower friction and better heat dissipation.
High-Temperature Solid Lubricants
Ceramic-Based Lubricants: Advanced ceramics, such as silicon nitride or boron nitride, offer excellent high-temperature stability and low friction, making them ideal for high-speed applications.
Benefits for Bearings: Bearings made with or coated in these materials maintain lubrication properties even at the elevated temperatures generated by high-speed operation.
Metal Matrix Composites (MMC)
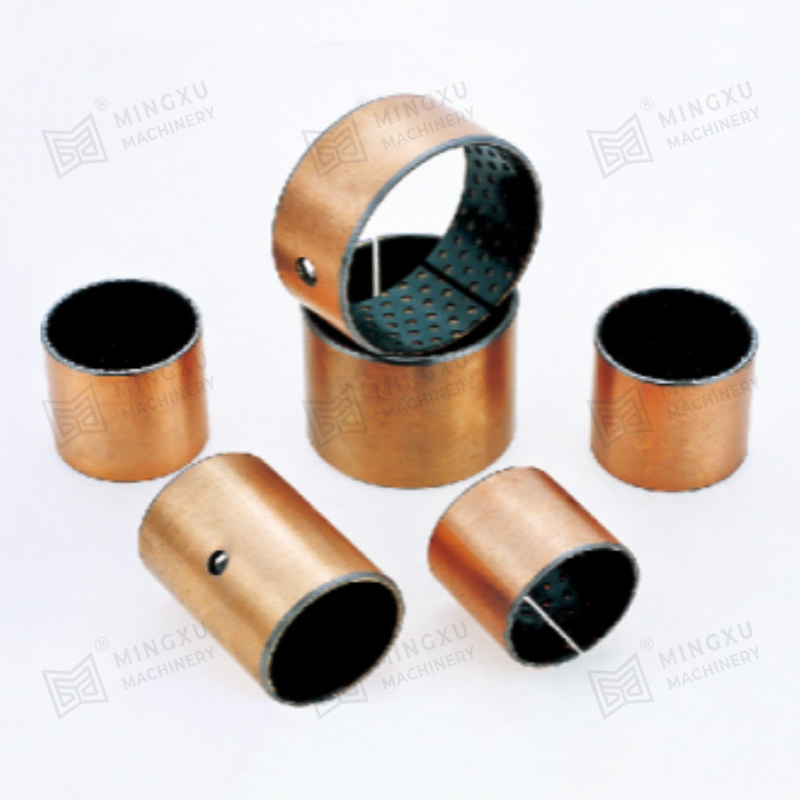
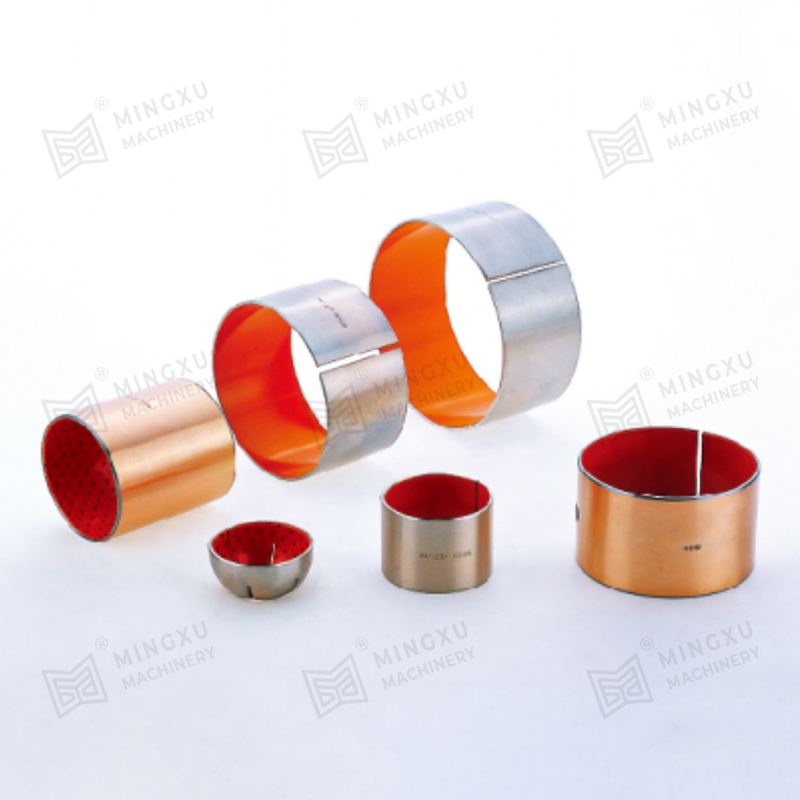
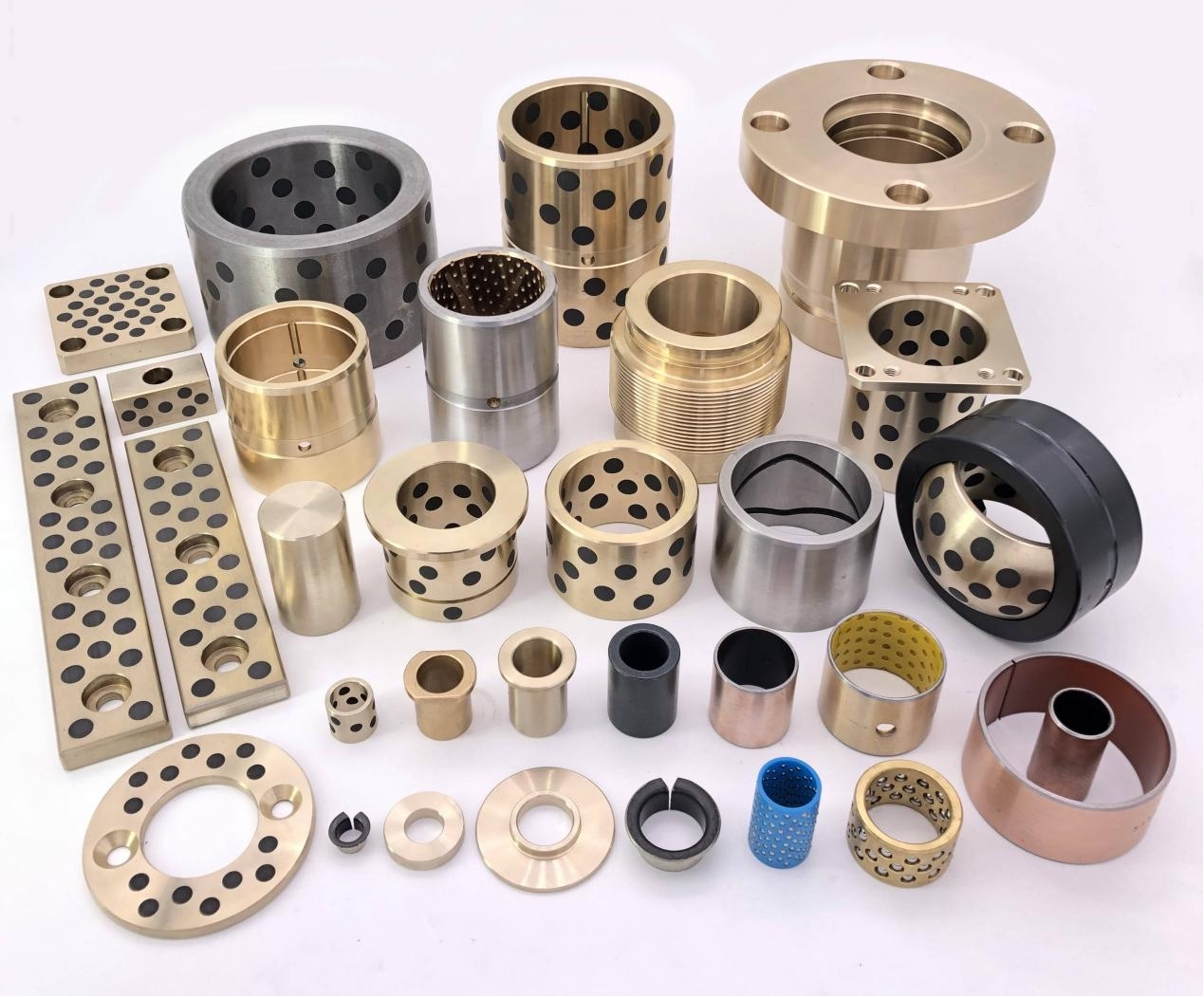
Lubricant Integration: Embedding solid lubricants (e.g., MoS₂ or graphite) directly into a metal matrix provides a strong, durable bearing material with self-lubricating properties.
Benefits for Bearings: This design improves wear resistance and ensures consistent lubrication even under high rotational speeds and loads.
Polymer Innovations
Enhanced Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): Modified PTFE with additives like glass fibers or carbon increases durability and reduces wear at high speeds.
Polymer Composites: New polymer blends infused with solid lubricants are being developed to combine flexibility, low friction, and high-speed performance.
Benefits for Bearings: These materials make solid-lubricating bearings lighter, quieter, and capable of withstanding the stresses of rapid motion.

Adaptive Solid Lubricants
Phase-Changing Materials: Some modern solid lubricants can change their structure at high temperatures or pressures to provide optimal lubrication dynamically.
Benefits for Bearings: These adaptive properties ensure that solid-lubricating bearings perform well across a range of operating speeds and conditions.
Surface Engineering and Coatings
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) Coatings: DLC coatings on solid-lubricating bearings reduce wear and friction significantly, even at very high speeds.
Advanced Plasma Spraying: This technique can deposit uniform, high-performance solid lubricant coatings on bearing surfaces, enhancing their durability and speed capabilities.
Hybrid Lubrication Approaches
Combination Systems: Bearings with both solid lubricant layers and microchannels for emergency liquid lubrication are being developed for ultra-high-speed applications.
Benefits for Bearings: This hybrid approach provides the stability of solid lubrication with added lubrication for extreme conditions.
Future Potential
The development of these materials is paving the way for solid-lubricating bearings that can:
Handle higher speeds without increasing maintenance requirements.
Operate in extreme conditions like aerospace, where high rotation rates and temperature variations are common.
Provide consistent performance and long lifespan, even under dynamic stresses.



















Nobis loquere